Radio waves of various different frequencies are used for mobile phone communications such as smartphones. Differences in frequency result in differences in the size of the communication area and communication speed. This article explains how differences in frequency bands result in differences in communication speed and communication area.
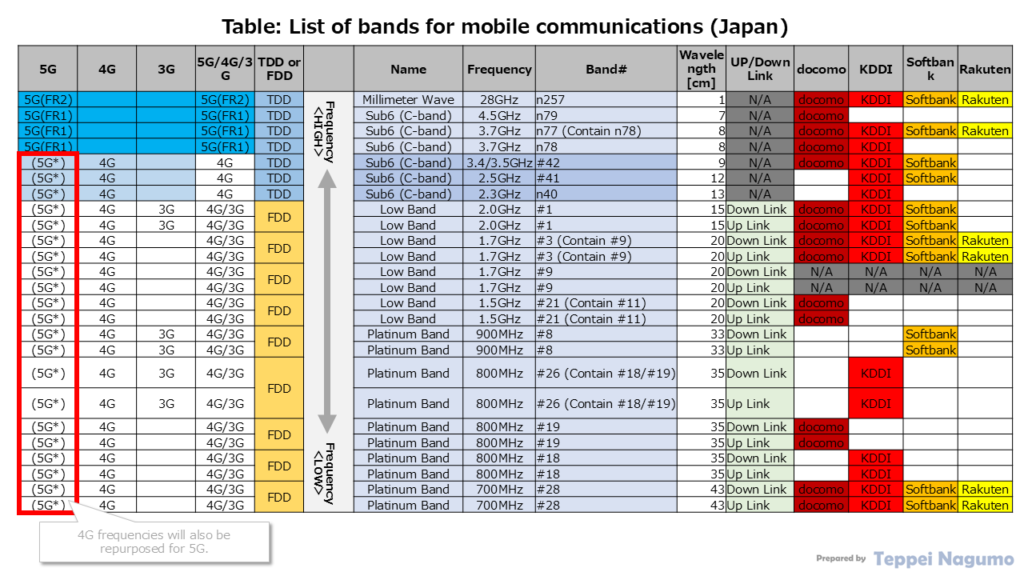
List of 5G/4G wireless bands (Example of Japanese telecommunications carriers)
Japanese telecommunications carriers NTT Docomo, KDDI, Softbank, and Rakuten Mobile use various frequency bands for mobile communications, as shown in the table below. The difference in the frequency band used has a significant impact on the communication area and communication speed.
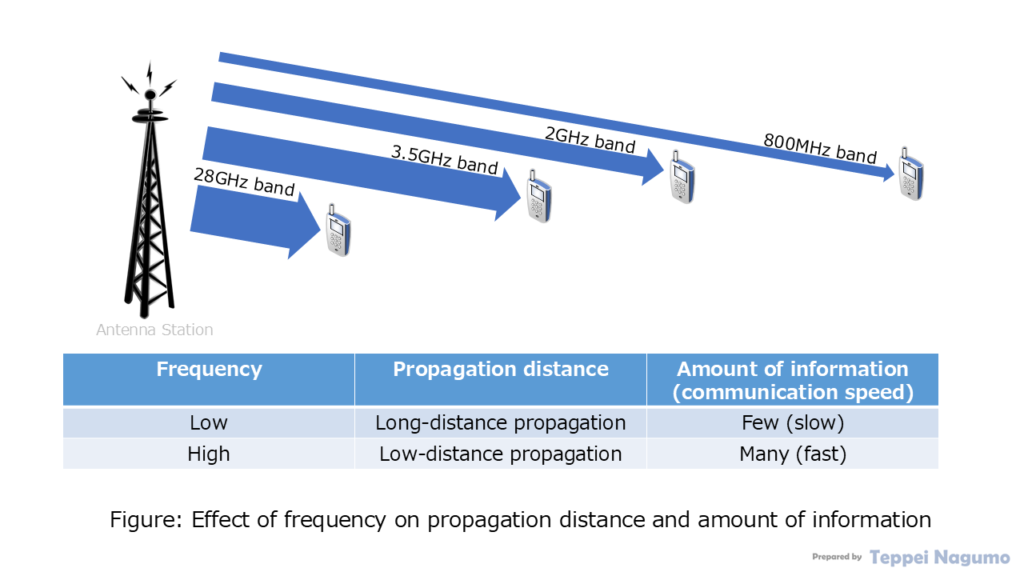
Low-frequency radio waves travel long distances. They are also less affected by buildings and obstacles. It is difficult to secure a wide bandwidth for low-frequency radio waves, so communication must be done with a narrow bandwidth. As a result, fast communication speeds cannot be achieved.
High-frequency radio waves travel long distances. They are also more easily affected by buildings and obstacles. It is easier to secure a wide frequency band for high-frequency radio waves, so communication speeds are faster. We will explain this in more detail in the following chapter.
Sub6 (3.7 GHz band, 3.5 GHz band, Frequency band below 6 GHz) and mmWave (Millimeter Wave: 28 GHz band) are frequencies exclusively for 5G, with wide frequency bands reserved for mobile communications.
In the lower frequency bands, such as the 800 MHz band and the 700 MHz band, only narrow frequency bands can be reserved for mobile communications.
For detailed bandwidth information on each frequency band allocated to each Japanese telecommunications carrier (Docomo, KDDI, Softbank, Rakuten Mobile), please refer to the following article.
Differences in wireless area and communication speeds due to differences in bands
Mobile communication radio waves cannot simultaneously satisfy both “fast communication speed” and “wide wireless area”. Here we explain the frequency bands used in specific mobile communication.
High frequencies (bands) such as millimeter waves (mmWave) can secure a wide frequency width for communication. (Bandwidth of 40MHz to 100MHz or more) Therefore, high communication speeds (user throughput) can be achieved. However, high frequencies (bands) such as millimeter waves (mmWave) are difficult to transmit and cannot secure a wide area. In addition, high frequencies (bands) such as millimeter waves (mmWave) are easily affected by buildings and obstacles.
Low frequency radio waves such as low bands and platinum bands cannot secure a wide frequency width for communication. Therefore, communication speeds (user throughput) are low. However, low frequency radio waves such as low bands and platinum bands can easily transmit far and secure a wide area. In addition, low frequency radio waves such as low bands and platinum bands are less affected by buildings and obstacles.
The diagram below summarizes the differences in frequencies for mobile communications and the differences in characteristics associated with each frequency.
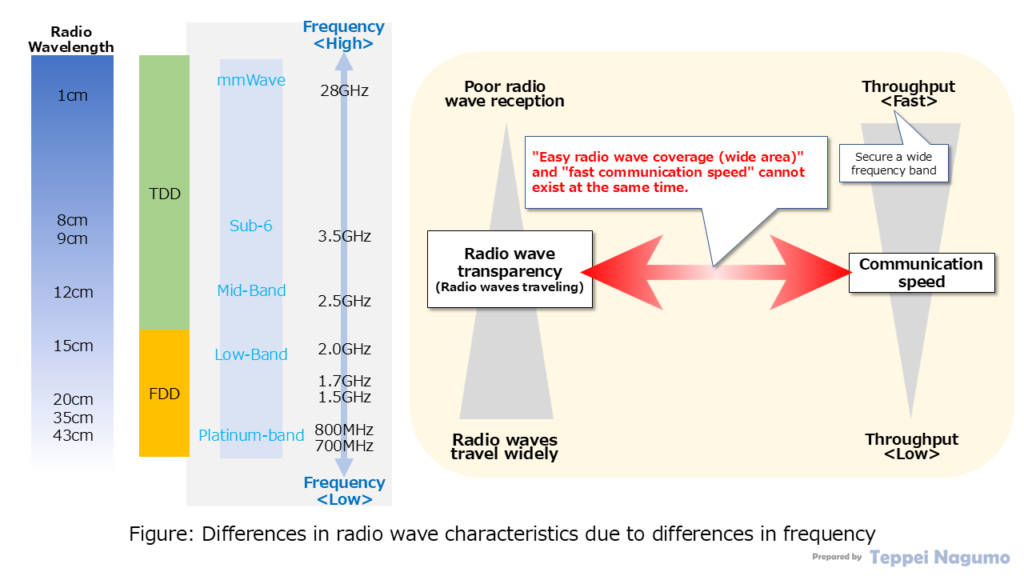
Differences in wireless coverage area and communication speeds due to differences in bands
The characteristics of the radio waves of millimeter waves (mmWave), which have started to be used in 5G mobile communications, and the platinum and low bands used in conventional 4G/3G are very different.
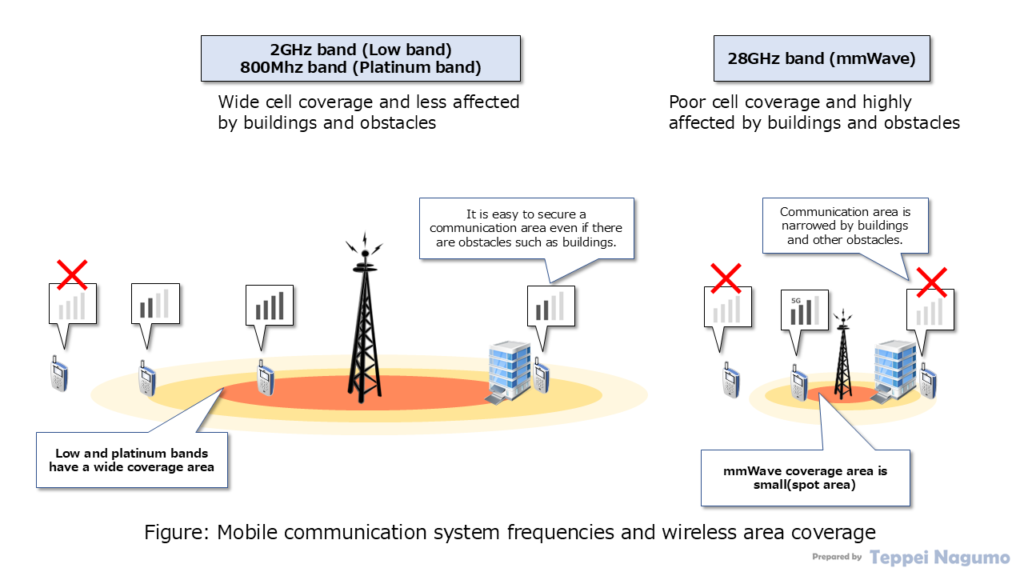
Millimeter Waves (28 GHz band in Japan) are strongly affected by buildings and obstacles. Therefore, it is difficult to secure a communication area inside a building or in the shadow of an obstacle.
Platinum bands and Low bands are less affected by buildings and obstacles. Therefore, it is possible to secure a communication area inside a building or in the shadow of an obstacle. Therefore, platinum and low bands can secure a wide communication area. This is why low-frequency radio waves for 4G LTE are being actively diverted for 5G NR in Japan.
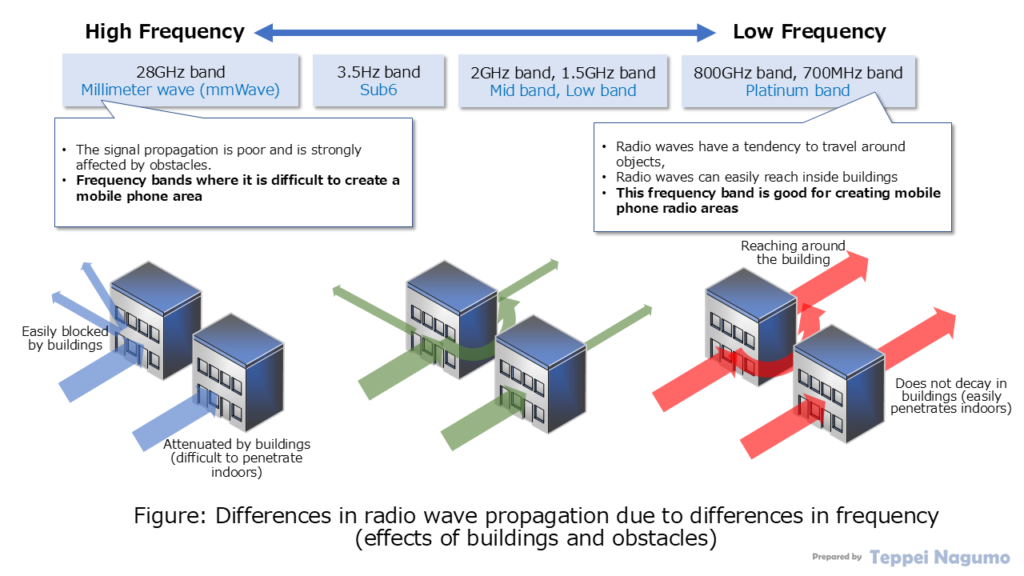
Differences in wireless communication area due to differences in bands
Platinum and low bands (low frequency bands) transmit radio waves over a wide range. A single radio unit (RU) can cover a wide area. At the same time, radio waves can easily reach areas shaded by buildings and obstacles.
Mobile communication wireless areas are created by devices called base stations (RU: Radio Unit). One outdoor macro base station covers a wireless area with a radius of several kilometers to ten of kilometers (in the case of low and platinum bands with low frequencies).
Millimeter waves (high frequency bands) do not transmit radio waves over a wide area. A single radio unit (RU) can cover a narrower area. At the same time, radio waves are affected by buildings and obstacles and are less likely to transmit.
When telecommunications carriers design wireless areas for mobile communications, they overlap radio waves of multiple frequencies. They also take into account the differences in radio wave characteristics due to different frequencies.
In urban areas and areas with high communication traffic, multiple frequencies are made available for simultaneous use. In particular, in places where people are mixed together, high frequency radio waves such as sub6 and millimeter waves are actively used. (See the diagram below)
In rural areas and sparsely populated areas, low frequency radio waves such as platinum bands are used. Low frequency radio waves have a wide range, and can secure coverage in every corner, including inside buildings and in the shadows of obstacles. (See the diagram below)
How exactly do communication speeds and wireless coverage differ depending on the band?
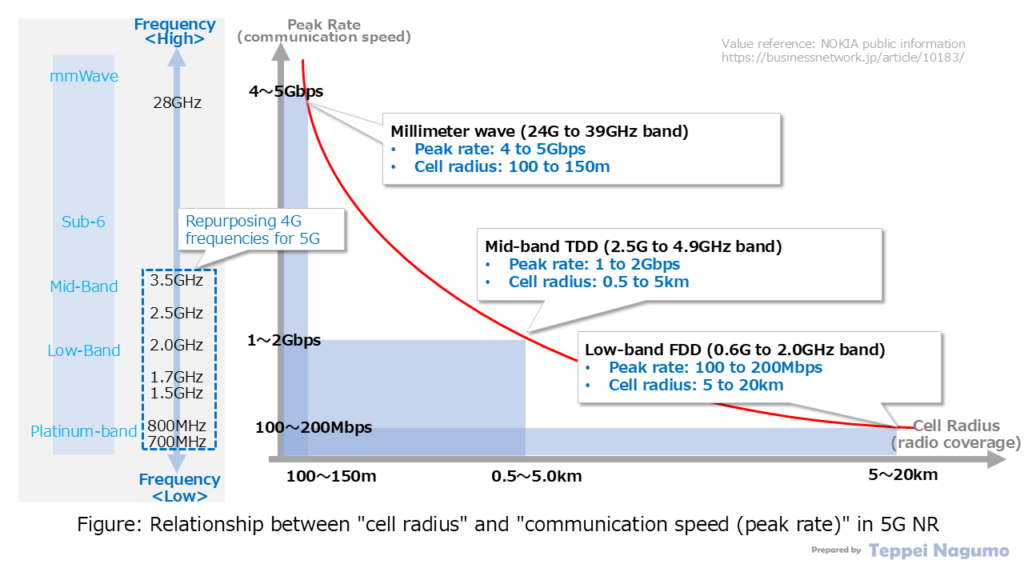
The figure below shows how communication speeds (peak speeds) differ specifically depending on the radio frequency (radio band) for 5G. The figure below also shows how wireless communication areas (cell coverage*) differ specifically depending on the radio frequency (radio band) for 5G.
(*Cell coverage: The radius of an area that can be wirelessly covered by one base station (wireless unit))
Millimeter wave (24GHz to 39GHz band)
- Peak communication speed rate: 4,000 to 5,000Mbps
- Radius: 100 to 150m
Low band FDD (0.6GHz to 2.0GHz band)
- Peak communication speed rate: 100 to 200Mbps
- Radius: 5,000 to 20,000m
Summary
This article explains the various different frequencies of radio waves used for wireless communication on smartphones and other devices. In this article, we have explained how differences in frequency bands cause differences in communication speeds and communication areas.
For details on the frequency bands owned by each telecommunications carrier, please refer to the following website.




コメント