What is 5G? This blog pot describes how a 5G Network can change from a 4G Network.
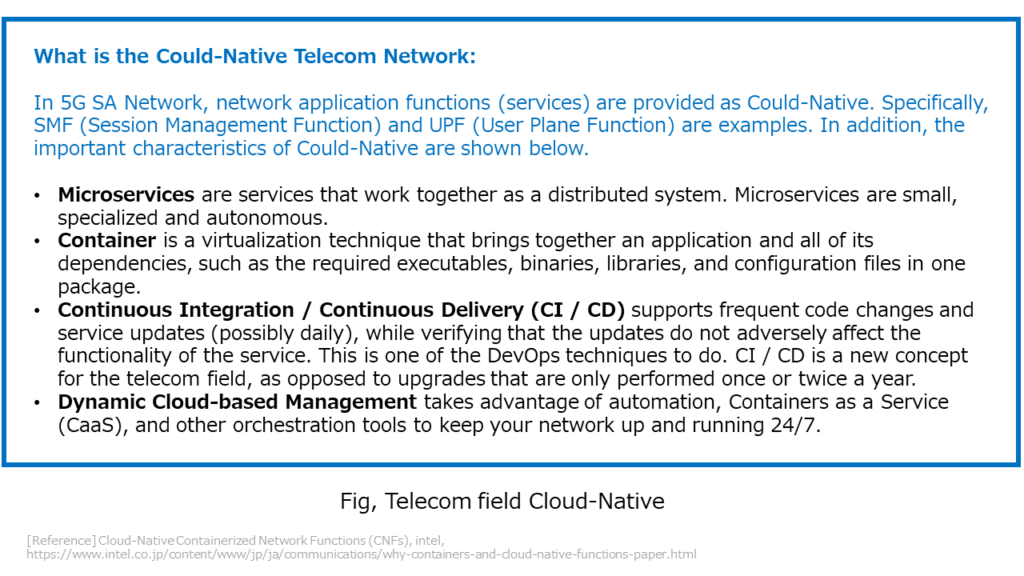
In 5G, general-purpose equipment (COST server: Commercial Off-The-Shelf server) and common software will be used for network equipment. Along with this, network virtualization (hardware and software are handled separately) and cloud computing (Could-Native) are being promoted. Describes 5G Network virtualization and Cloud conversion (Could-Native).
What is Network Virtualization?
A 4G or 3G network consists of dedicated software that runs on that dedicated device. In 5G, general-purpose equipment (COST server: Commercial Off-The-Shelf server) will be used, and a common software platform will be used. As a result, the network will be virtualized by separating the device (Hardware) and software and handling.
Just as virtual machine and computers are widely used, 5G will allow us to configure virtual networks. With the spread and evolution of 5G, the development methods and technologies used in the Cloud field are also being used in the 5G Telecom field. Along with that, the network is becoming cloud-based.
Network virtualization: From PNF (Physical Network Function) to VNF (Virtual Network Function)
The transition from PNF (Physical Network Function), which implements individual network functions on a dedicated physical device, to VNF (Virtual Network Function), which implements a virtualized network function on a general-purpose physical server, is progressing. VNF (Virtual Network Function) is a virtual network function based on NFV (Network Function Virtualization).
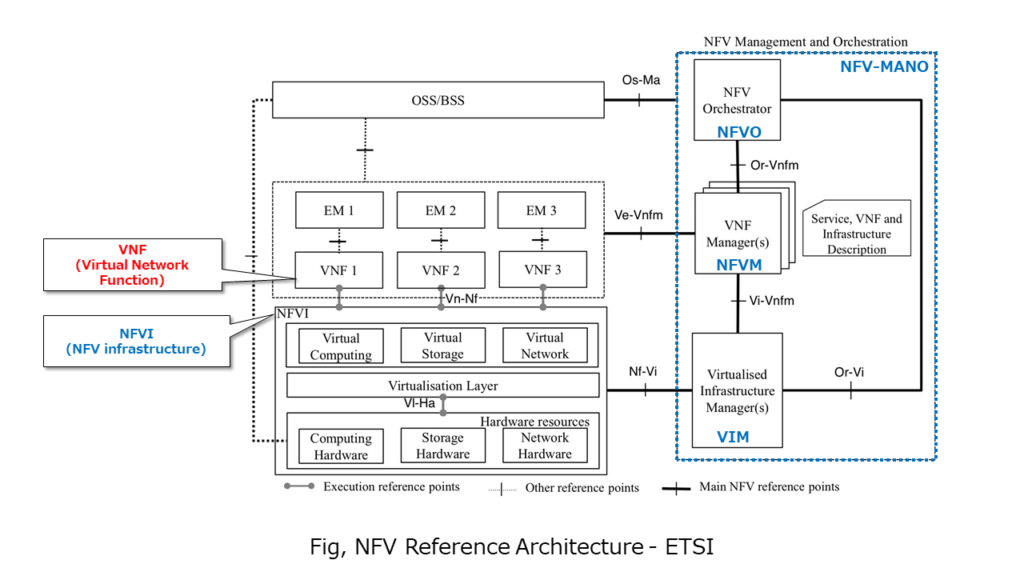
With the progress of network migration to VNF, telecom industry was able to shorten the procurement time for network equipment (Hardware). On the other hand, at the same time, there is a problem that the operation of VNF becomes complicated.
Cloud-Native Network: VNF (Virtual Network Function) to CNF (Cloud-Native Network Function)
What is CNF?
The transition from VNF (Virtual Network Function) to CNF (Cloud-Native Network Function), which implements cloud-native network functions on cloud environments, is progressing. With 5G, CNF conversion will progress. CNF is a network function that runs on the open source container orchestration system “Kubernetes (K8s)“. Kubernetes is a system for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications. A system designed by Google and currently being maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
CNF is a network environment virtualized by containerization. Unlike conventional virtualization VMs (Virtual Machines), virtualization of container environments has various advantages in terms of efficiency of development. The container environment has characteristic such as “easy to distribute the developed and created environment” and “easy to scrap and build”, and innovation is accelerating from the development side. Docker, an open source platform, is widely used for container virtualization.
The application of cloud-native technologies such as Service-mesh and Micro-service is advancing in the 5G Telecom field. 5G Core uses cloud-native technology as one of the purposes of streamlining network function development.
If you would like to know more about CNF in the Telecom field, please refer to the Technical Report below (reference).
White paper – Why use container and could-native function anyway? Intel [PDF file]
Characteristic and benefits of Could-Native
Below is a summary level of the benefits of Could-Native over 5G Networks.

Below is a summary level of notable characteristic of Could-Native Network in 5G Network.
Organizations and groups promoting CNF
The open source promotion organizations CNCF (Cloud Native Computing Foundation) and LF Networking (Linux Foundation Networking) have announced a policy to promote the transition from VNF (Virtual Network Function) to CNF (Cloud native Network Function). CNF is expected to become one of the core technologies in 5G networks.

CNFC (Cloud Native Computing Foundation) [Website]

LFNetworking (Linux Foundation Networking) [Website]
The Linux Foundation (LF) is a non-profit technology consortium founded in 2000 by the merger of Open Source Development Labs and Free Standards Group. LF is promoting Linux technology development and industry adoption with the goal of “promoting Linux growth by providing a variety of services to compete with closed platforms.”

Linux Foundation [Website]
The following blog post summarizes the open source projects related to the OPEN interface of the Network, which is being promoted with the participation of the Linux Foundation.
SBA (Service Based Architecture) 5G Core
The 5G Core Network uses SBA (Service Based Architecture), which is widely used in the Cloud field. In 4G Core (EPC: Evolved Packet Core), point-to-point reference points were individually defined between devices.
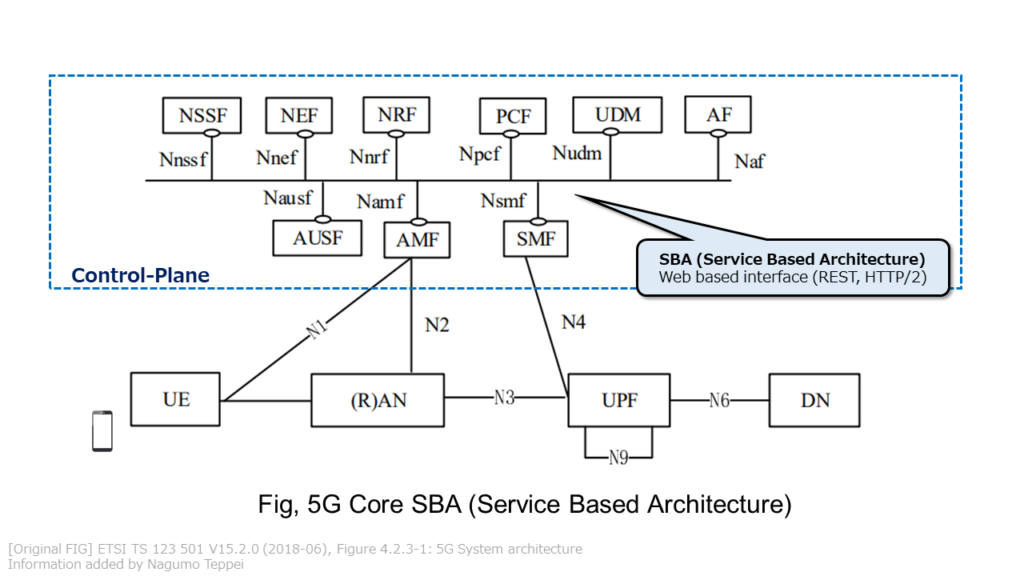
In 5GC (5G Core), each function of Core is regarded as a service, and the interface between each function (service) is unified to Web-based Interface (HTTP / Rest). SAB is a bus-type micro-service architecture in which 5G Core functions are connected to each other. Microservices architecture is a technology used in the Cloud field, and efficiency is achieved by adopting it in 5G Network.
In 5GC (5G Core), the microservices architecture adopted in the Cloud field has been applied to the 3GPP standard in the Telecom field. The following documents provide detailed information on 5G Core’s microservices architecture and 5G Core features (reference).
Summary
I explained how a 5G network changes from a 4G network in terms of network virtualization and Could-Native.
In 5G, as network virtualization progresses, network devices (Hardware) and software will be handled separately. As a result, the number of players who provide network equipment and software will increase, and multi-vendor will progress.
With the advancement of 5G Network as Could-Native, the technologies, development methods, and service deployment methods already used in the Could field can be used as they are in the 5G Telecom field, resulting in significant development and service deployment efficiency. It is believed that the conversion will progress.
![[Reference] unsplash, Rafael Garcin, https://unsplash.com/photos/4iECeLWtt5E](https://teppeilog.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Cloud_Eyec.png)




コメント