This blog post describes RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller), which is a 5G wireless network technology. RIC is a technology that makes radio access networks (RANs) more open and intelligent. AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning) is used for RIC. As a result, the operation of mobile networks that use RIC will be streamlined and automated.
The O-RAN alliance, an organization of carriers and telecommunications equipment vendors, is standardizing RIC. RIC will open up RAN technical specifications and interfaces, and at the same time make RAN functions intelligent.
RIC Concept (Equipped with AI/ML as standard)
RAN (Radio Access Network) is a 5G and 4G radio access network. RAN controls the wireless conectivity of 5G NR and 4G LTE networks. RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) optimizes the radio resources of the RAN and automates the operation of the RAN.
Below is an overview of the RIC architecture and the RIC concept. The concept of RIC incorporates the concept of SDN (Software Defined Network).
- [RIC Concept]
- Automation of RAN operations
- Intelligent RAN function
- Optimization of RAN processing resources and radio resources
- Programmable software function
- Open interface
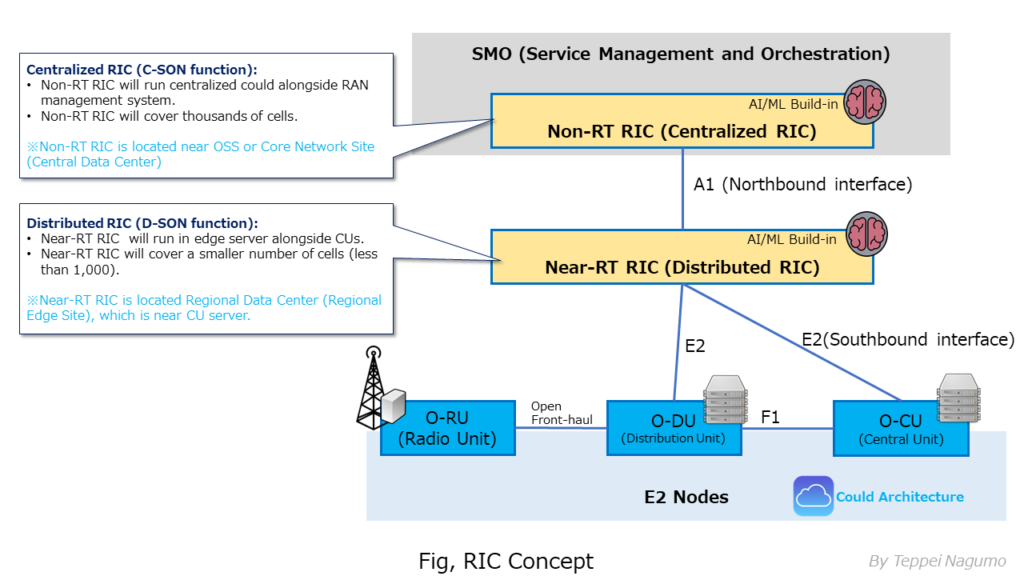
RIC is one of the key components of RAN. RIC is a controller that manages and controls software on nodes and devices such as RU (Radio Unit), DU (Distributed Unit), and CU (Centralized Unit) that make up 5G RAN. The RIC itself is also composed of multiple components and is implemented by software. The interface of RIC is OPEN and standardized. With this opening, many new players have entered the RAN market and are becoming multi-vendors.
RIC is premised on the use of AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning). RIC makes RAN functions and their operation methods intelligent. RIC enhances 5G services and improves operational efficiency through intelligent functions such as connectivity performance, quality monitoring and optimization.
RIC Use Cases
The function of RIC replaces the function of SON (Self-Organized Network) of the traditional network. SON is a network function that automates and optimizes settings in 4G and 3G mobile networks. At the same time, RIC realizes more intelligent new network functions.
Introducing some typical RIC Use Cases. In addition to the RIC Use Cases listed below, RIC envisions a number of different 5G and 4G network services and new uses.
Personalized Service and Quality of Experiences by RIC
RIC provides different required quality wireless connections for each user (terminal or session). In addition, RIC optimizes RAN processing resources and wireless connection control (Beamforming, Massive-MIMO control, etc.) using multiple antennas. This improves the user experience (QoE: Quality of Experience). RIC optimizes communication for each network slice (a set of virtualized network processing resources).
For more information on Network Slice, please refer to the following blog post.
Reducing Network Cost (CAPEX and OPEX) by RIC
RIC reduces operating costs for 5G and 4G Network RAN part. With the opening of the 5G Network, multiple new players will enter the market and become multi-vendor, reducing 5G and 4G RAN equipment and software costs (CAPEX). In addition, RIC’s 5G and 4G RAN operational efficiency and automation will reduce network operating costs (OPEX).
New Revenue for Operators (Carriers)
The intelligent function of RIC enables carriers to control the network slice of RAN considering SLA (Service Level Agreement). As a result, carriers will be able to provide a variety of network services that have never been seen before. In other words, carriers can create a new source of revenue.
What is O-RAN alliance? What is ONF(Open Network Foundation)?
RIC standardization promoted by O-RAN alliance
RIC is being standardized by the O-RAN alliance. The O-RAN alliance is an organization that aims to make the next generation RAN more scalable, more open and intelligent. O-RAN alliance is an organization in which telecommunications carriers and telecommunications equipment vendors participate.
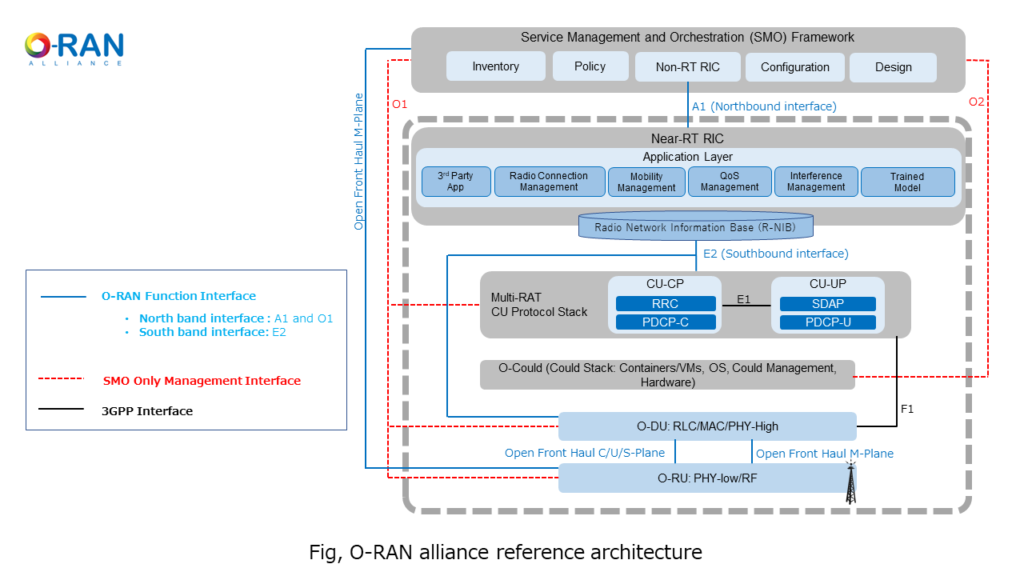
- [Glossary of above figure]
- CP: Control Plane
- MAC: Media Access Control
- MANO: Management and Orchestration
- NFVI: Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure
- ONAP: Open Network Automation Platform
- PDCP: Packet Data Convergence Protocol
- O-Cloud: Orchestration and Cloud Platform
- PHY: Physical Layer
- RAT: Radio Access Technology
- RF: Radio Frequency
- RLC: Radio Link Control
- RRC: Radio Resource Control
- SDAP: Service Data Adaptation Protocol
- UP: User Data Plane
Please refer to the following blog post for details on the opening of the Network and the activities of ORAN alliance.
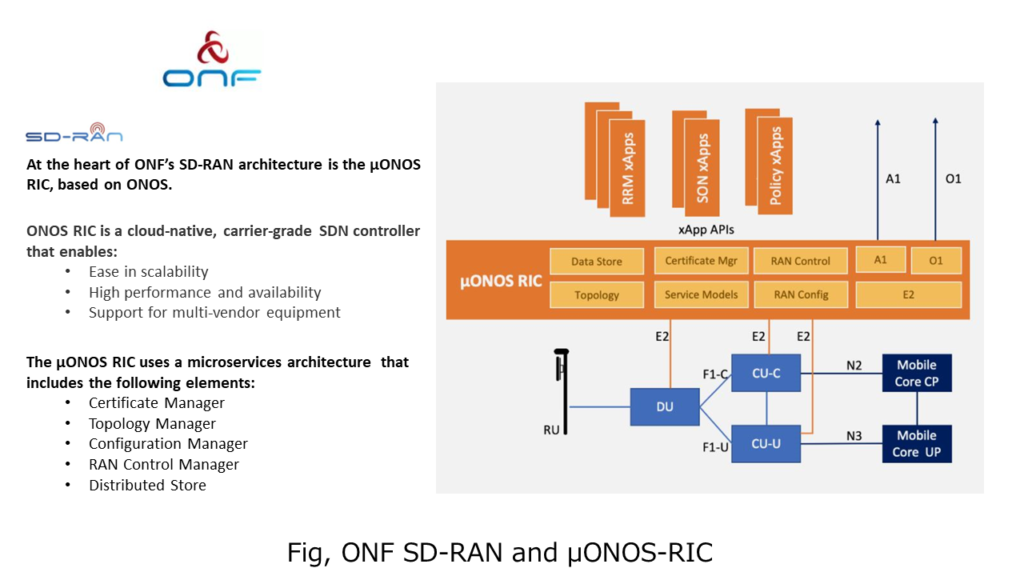
SD-RAN project promoted by ONF
ONF (Open Networking Foundation) has created the SD-RAN (Software Defined Radio Access Network) project to support the development of opensource software platforms and multi-vendor solutions for 5G and 4G RAN deployments. This SD-RAN project is an activity similar to the RIC of the O-RAN alliance.
ONF is a non-profit carrier-led consortium. ONF is an organization that drives the transformation of network infrastructure and telecommunications carriers’ business models through research, development and education.
ONF (Open Network Foundation), [official website]
In ONF, the function corresponding to Near-RT RIC of O-RAN alliance is μONOS RIC. μONOS RIC is cloud-native designed (designed based on container technology) and supports scalability (expansion/reduction according to traffic) and high performance as well as real-time functions required for intelligent RAN control.
In addition to ONF, TIP (Telecom Infrastructure Project) RIA (RAN intelligent and Automation) subgroup is active in xAPP and rAPP development (examination of RIC use cases), testing and deployment.
TIP, Near-real-time RIC: enabling AI/ML-driven extreme automation and granular control of Open RAN, [Web Link]
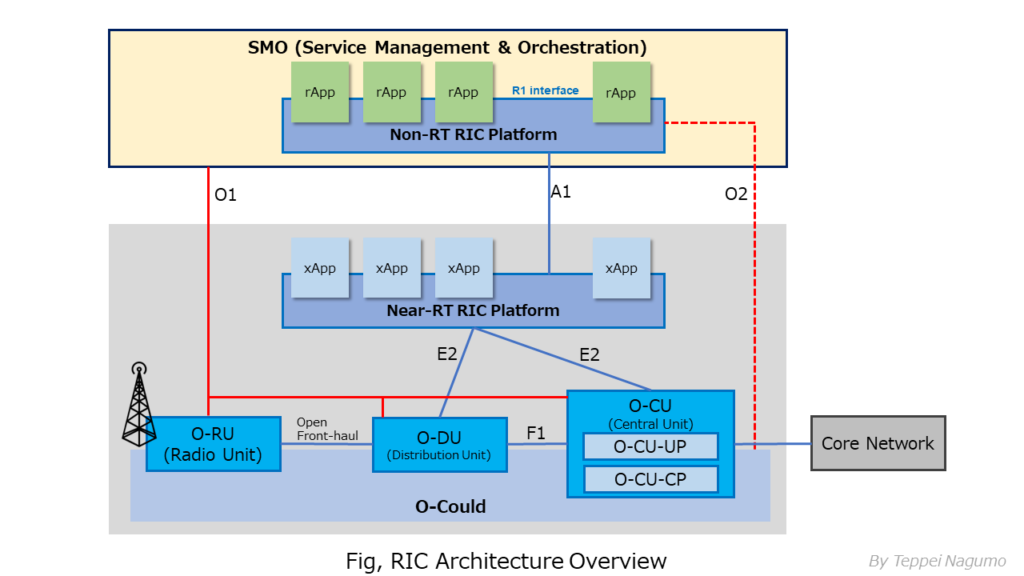
RIC Architecture
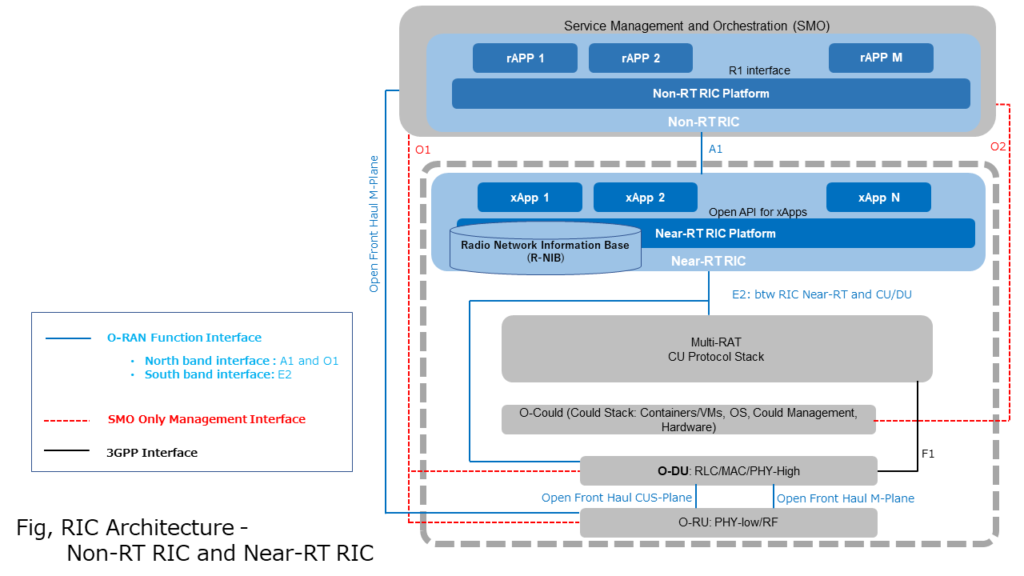
RIC is divided into Near-RT-RIC (real-time RIC) and Non-RT-RIC (non-real-time RIC). See the figure below in detail.
What is Non-RT-RIC (Non Real Time RIC)?
Non-RT RIC (Non Realtime RIC) is also known as Centralized RIC. One Non-RT RIC controls several thousand wireless cells. Non-RT RIC is located with or near a central cloud station such as OSS (Operation Support System).
Non-RT RIC (Non Realtime RIC) generates and notifies policies related to RAN control, and transfers information to Near-RT RIC. Non-RT RIC is located inside SMO (Service Management and Orchestration) that manages and orchestrate RAN.
Policies generated by Non-RT RIC are expressed in the form of quality of service (QoS) and user experience (QoE) provided by RAN. This policy is analyzed and generated based on the information collected from base stations (O-Could) and terminals.
Non-RT RIC is divided into an application called rAPP (Non-RT RIC Application) for analyzing various information and generating policies, and a Non-RT RIC platform that operates multiple rAPPs at the same time. The rAPP and the Non-RT RIC platform are connected by the R1 interface specified by the O-RAN alliance.
What is Near-RT-RIC(Near Real Time RIC)?
Near-RT RIC (Near Realtime RIC) is also known as Distributed RIC. Near-RT RIC (Near Realtime RIC) covers about 1000 or less wireless cells. The Near-RT RIC function is installed near the CU. In some cases, one Near-RT RIC function covers multiple CUs.
Near-RT RIC (Near Realtime RIC) is located near the RAN node (RU, CU, DU) and intelligently controls the RAN node and RAN processing resources.
Near-RT RIC is divided into a dedicated microservices-based application xAPP(Near Realtime RIC Application) and the Near-RT RIC platform part that runs multiple xAPPs at the same time. Near-RT RIC receives policy guidance from Non-RT RIC and provides policy feedback to Non-RT RIC through a dedicated application of xAPP.
The figure below shows the relationship between rAPP and Non-RT RIC Platform, and the relationship between xAPP and Near-RT RIC Platform.
Difference in processing time between Non-Realtime RIC and Near-Realtime RIC
In RIC, the control processing time required for RIC control loop processing differs for each layer. The closer to the RAN node of RU, DU, CU, the shorter the allowable processing time.
The hierarchy of the RIC control loop is divided into “Non-RT RIC layer”, “Near-RT RIC layer”, and “DU, CU node layer” from the top. The processing time allowed by the RIC control loop becomes shorter from the upper layer to the lower layer. (See the figure below.)
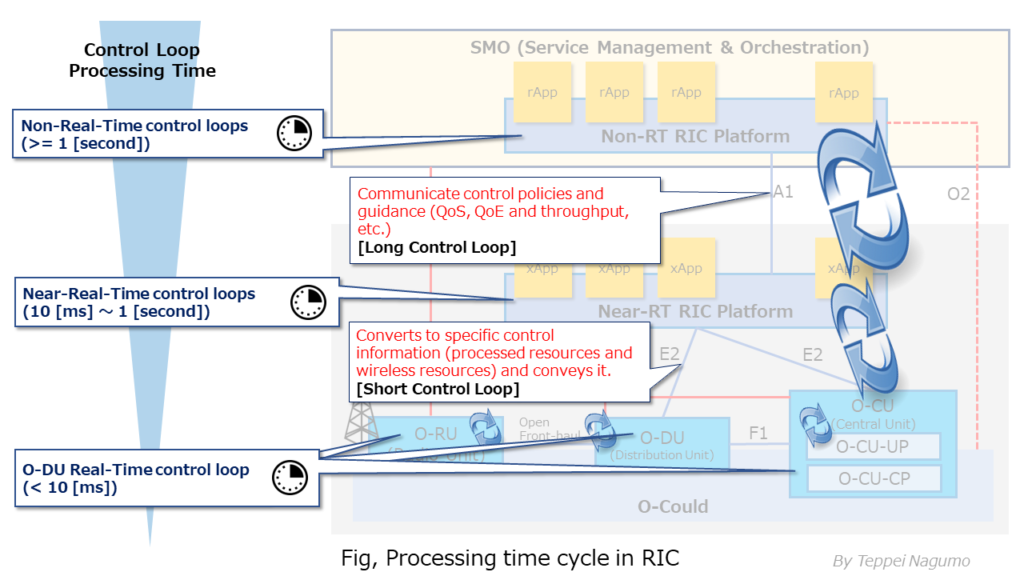
The DU protocol processing is near real-time processing that allows only a processing delay of about 10 nano-seconds. DU performs protocol processing that requires near real-time processing. The delay allowed for Layer 2 protocol processing performed by DU is the strictest, and only a processing delay of about 10 nano-seconds is allowed.
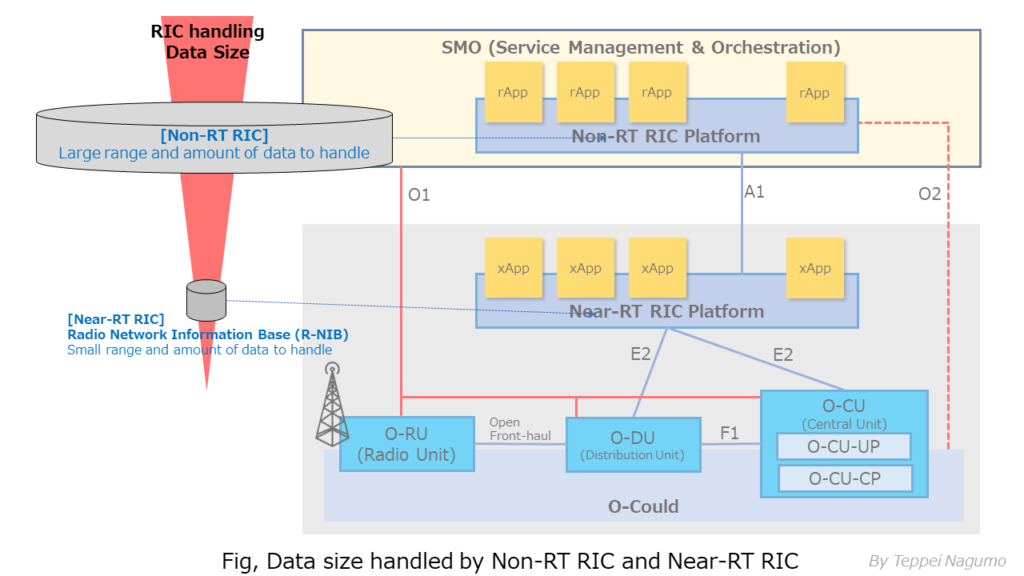
Data volume and data range handled by RIC
In RIC, the range and amount of data handled processing time by Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC are different. This is related to the processing time allowed by RIC.
The non-RT RIC hierarchy allows a long processing time of 1 second or more in the RIC processing control loop. Non RT RIC handles a wider range of data than Near-RT RIC, and handles more data.
On the other hand, the Near RT RIC hierarchy allows only 10 ms to 1 second of processing time in the RIC processing loop. This is because Near RT RIC needs to consider protocol processing performed on CU and DU nodes, which require more short processing time. In addition, Near-RT RIC handles a narrower range of data than Non-RT RIC, limiting the amount of data that needs to be processed and analyzed.
Summary
This blog post described the RIC, 5G and 4G wireless network technology. RIC is a technology that makes radio access network (RAN) open and intelligent. RIC has opened the RAN interface and made it multi-vendor. In addition, RIC will make RAN intelligent, streamline and automate RAN operations.
RIC technology is deeply related to Virtual-RAN (VRAN), which makes the RAN function software, and Open-RAN (ORAN), which opens the interface and technology. RIC technology is based on these VRANs and ORANs.





コメント